How To Treat A Sore Achilles Tendon
Overview
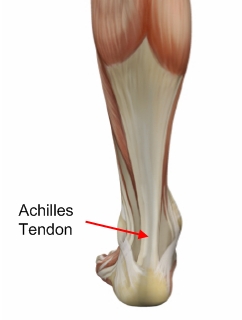 The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscles in the lower leg to the heel bone. It is the largest yet most exposed tendon in the body. Achilles tendonitis is where the Achilles tendon, and sometimes the protective sheath through which it moves, becomes inflamed, causing pain and swelling symptoms. Achilles tendonitis (also known as Achilles tendinopathy or tendonosis) is classified as an overuse injury. If left untreated it can become chronic (long-term), requiring more intensive treatment. Achilles tendonitis can also increase the risk of sustaining an Achilles tendon rupture (tear).
The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscles in the lower leg to the heel bone. It is the largest yet most exposed tendon in the body. Achilles tendonitis is where the Achilles tendon, and sometimes the protective sheath through which it moves, becomes inflamed, causing pain and swelling symptoms. Achilles tendonitis (also known as Achilles tendinopathy or tendonosis) is classified as an overuse injury. If left untreated it can become chronic (long-term), requiring more intensive treatment. Achilles tendonitis can also increase the risk of sustaining an Achilles tendon rupture (tear).
Causes
There are hundreds of tendons scattered throughout our body, but it tends to be a small handful of specific tendons that cause problems. These tendons usually have an area of poor blood supply that leads to tissue damage and poor healing response. This area of a tendon that is prone to injury is called a "watershed zone," an area when the blood supply to the tendon is weakest. In these watershed zones, they body has a hard time delivering oxygen and nutrients necessary for tendon healing, that's why we see common tendon problems in the same parts of the body. Tendonitis is most often an overuse injury. Often people begin a new activity or exercise that causes the tendon to become irritated. Tendon problems are most common in the 40-60 year old age range. Tendons are not as elastic and forgiving as in younger individuals, yet bodies are still exerting with the same force. Occasionally, there is an anatomical cause for tendonitis. If the tendon does not have a smooth path to glide along, it will be more likely to become irritated and inflamed. In these unusual situations, surgical treatment may be necessary to realign the tendon.
Symptoms
If you have Achilles tendinitis or Achilles enthesopathy, you are likely to experience the following symptoms. Pain. You may notice aching, burning, or tearing pains at the back of your heel or above the ankle. The pain can range from mild to very severe and disabling. It is most noticeable in the following circumstances. After resting. Many people report that pain increases when they first get out of bed in the morning or after sitting for a period of time. After exercise. Pain may increase if you exercise or stand for a period of time. A lump. In some cases, a tender lump can develop at the site of the injured tendon (tendinosis). Bone spurs. When the injury occurs at the point where the tendon attaches to the foot, a bone spur may develop on the heel.
Diagnosis
On examination, an inflamed or partially torn Achilles tendon is tender when squeezed between the fingers. Complete tears are differentiated by sudden, severe pain and inability to walk on the extremity. A palpable defect along the course of the tendon. A positive Thompson test (while the patient lies prone on the examination table, the examiner squeezes the calf muscle; this maneuver by the examiner does not cause the normally expected plantar flexion of the foot).
Nonsurgical Treatment
Self-care strategies include the following steps, often known by the acronym R.I.C.E, Rest. You may need to avoid exercise for several days or switch to an activity that doesn't strain the Achilles tendon, such as swimming. In severe cases, you may need to wear a walking boot and use crutches. Ice. To decrease pain or swelling, apply an ice pack to the tendon for about 15 minutes after exercising or when you experience pain. Compression. Wraps or compressive elastic bandages can help reduce swelling and reduce movement of the tendon. Elevation. Raise the affected foot above the level of your heart to reduce swelling. Sleep with your affected foot elevated at night.

Surgical Treatment
There are two types of Achilles repair surgery for tendonitis (inflammation of the Achilles Tendon), if nonsurgical treatments aren't effective. Gastrocnemius recession - The orthopaedic surgeon lengthens the calf muscles to reduce stress on your Achilles tendon. D?bridement and repair - During this procedure, the surgeon removes the damaged part of the Achilles tendon and repairs the remaining tendon with sutures or stitches. Debridement is done when the tendon has less than 50% damage.
Prevention
Wear shoes that fit correctly and support your feet: Replace your running or exercise shoes before the padding or shock absorption wears out. Shock absorption greatly decreases as the treads on the bottoms or sides of your shoes begin to wear down. You may need running shoes that give your foot more heel or arch support. You may need shoe inserts to keep your foot from rolling inward. Stretch before you exercise: Always warm up your muscles and stretch gently before you exercise. Do cool down exercises when you are finished. This will loosen your muscles and decrease stress on your Achilles tendon. Exercise the right way: If your tendinitis is caused by the way that you exercise, ask a trainer, coach, or your caregiver for help. They can teach you ways to train or exercise to help prevent Achilles tendinitis. Do not run or exercise on uneven or hard surfaces. Instead, run on softer surfaces such as treadmills, rubber tracks, grass, or evenly packed dirt tracks.
 The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscles in the lower leg to the heel bone. It is the largest yet most exposed tendon in the body. Achilles tendonitis is where the Achilles tendon, and sometimes the protective sheath through which it moves, becomes inflamed, causing pain and swelling symptoms. Achilles tendonitis (also known as Achilles tendinopathy or tendonosis) is classified as an overuse injury. If left untreated it can become chronic (long-term), requiring more intensive treatment. Achilles tendonitis can also increase the risk of sustaining an Achilles tendon rupture (tear).
The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscles in the lower leg to the heel bone. It is the largest yet most exposed tendon in the body. Achilles tendonitis is where the Achilles tendon, and sometimes the protective sheath through which it moves, becomes inflamed, causing pain and swelling symptoms. Achilles tendonitis (also known as Achilles tendinopathy or tendonosis) is classified as an overuse injury. If left untreated it can become chronic (long-term), requiring more intensive treatment. Achilles tendonitis can also increase the risk of sustaining an Achilles tendon rupture (tear).
Causes
There are hundreds of tendons scattered throughout our body, but it tends to be a small handful of specific tendons that cause problems. These tendons usually have an area of poor blood supply that leads to tissue damage and poor healing response. This area of a tendon that is prone to injury is called a "watershed zone," an area when the blood supply to the tendon is weakest. In these watershed zones, they body has a hard time delivering oxygen and nutrients necessary for tendon healing, that's why we see common tendon problems in the same parts of the body. Tendonitis is most often an overuse injury. Often people begin a new activity or exercise that causes the tendon to become irritated. Tendon problems are most common in the 40-60 year old age range. Tendons are not as elastic and forgiving as in younger individuals, yet bodies are still exerting with the same force. Occasionally, there is an anatomical cause for tendonitis. If the tendon does not have a smooth path to glide along, it will be more likely to become irritated and inflamed. In these unusual situations, surgical treatment may be necessary to realign the tendon.
Symptoms
If you have Achilles tendinitis or Achilles enthesopathy, you are likely to experience the following symptoms. Pain. You may notice aching, burning, or tearing pains at the back of your heel or above the ankle. The pain can range from mild to very severe and disabling. It is most noticeable in the following circumstances. After resting. Many people report that pain increases when they first get out of bed in the morning or after sitting for a period of time. After exercise. Pain may increase if you exercise or stand for a period of time. A lump. In some cases, a tender lump can develop at the site of the injured tendon (tendinosis). Bone spurs. When the injury occurs at the point where the tendon attaches to the foot, a bone spur may develop on the heel.
Diagnosis
On examination, an inflamed or partially torn Achilles tendon is tender when squeezed between the fingers. Complete tears are differentiated by sudden, severe pain and inability to walk on the extremity. A palpable defect along the course of the tendon. A positive Thompson test (while the patient lies prone on the examination table, the examiner squeezes the calf muscle; this maneuver by the examiner does not cause the normally expected plantar flexion of the foot).
Nonsurgical Treatment
Self-care strategies include the following steps, often known by the acronym R.I.C.E, Rest. You may need to avoid exercise for several days or switch to an activity that doesn't strain the Achilles tendon, such as swimming. In severe cases, you may need to wear a walking boot and use crutches. Ice. To decrease pain or swelling, apply an ice pack to the tendon for about 15 minutes after exercising or when you experience pain. Compression. Wraps or compressive elastic bandages can help reduce swelling and reduce movement of the tendon. Elevation. Raise the affected foot above the level of your heart to reduce swelling. Sleep with your affected foot elevated at night.

Surgical Treatment
There are two types of Achilles repair surgery for tendonitis (inflammation of the Achilles Tendon), if nonsurgical treatments aren't effective. Gastrocnemius recession - The orthopaedic surgeon lengthens the calf muscles to reduce stress on your Achilles tendon. D?bridement and repair - During this procedure, the surgeon removes the damaged part of the Achilles tendon and repairs the remaining tendon with sutures or stitches. Debridement is done when the tendon has less than 50% damage.
Prevention
Wear shoes that fit correctly and support your feet: Replace your running or exercise shoes before the padding or shock absorption wears out. Shock absorption greatly decreases as the treads on the bottoms or sides of your shoes begin to wear down. You may need running shoes that give your foot more heel or arch support. You may need shoe inserts to keep your foot from rolling inward. Stretch before you exercise: Always warm up your muscles and stretch gently before you exercise. Do cool down exercises when you are finished. This will loosen your muscles and decrease stress on your Achilles tendon. Exercise the right way: If your tendinitis is caused by the way that you exercise, ask a trainer, coach, or your caregiver for help. They can teach you ways to train or exercise to help prevent Achilles tendinitis. Do not run or exercise on uneven or hard surfaces. Instead, run on softer surfaces such as treadmills, rubber tracks, grass, or evenly packed dirt tracks.