Pain In The Arch Of My Foot When I Walk
The arch of the foot is made from a complex series of bones tendons and ligaments. According to podiatric practice there is only one important arch of the foot on the medial side. The height of the arch varies and having a flat foot or high arched foot is inherited. The arch acts to dissipate forces and store energy within the foot. Most young children have flat feet and this is because the arch has fatty tissue overlying it. Normally an arch appears after the age of 5-6 years. Even if you remain flat footed this might be normal for you and your family. Just because the arch is low does not mean that any treatment is required. Many world class athletes have flat feet. If the arch is painful or the arch of one foot suddenly drops then investigation and treatment may be required. The arch might drop acutely due to a tear in a tendon or the movement of a bone within the arch. A scan and X Ray may be indicated and treatment ranging from insoles to surgery may be required. If you have a high arched foot this is likely to have been inherited. In extreme form this can cause pain in the ball of the foot and is often associated with a tight Achilles tendon and a tendency to walk on the outside of your foot. In most people there are no symptoms and in others there may pain along the arch and pain on the outside of your ankle. Both these foot types are often mild and require no treatment, but if symptoms occur a full bio-mechanical examination will often reveal a mechanical cause to your pain. Often the treatment may be simple stretches and orthoses.

Causes
The number one cause of arch pain is Plantar Fasciitis, and you'll be glad to know that more than 90% of cases of this painful condition can be resolved with simple, conservative at-home treatments. While extremely severe cases of Plantar Fasciitis may require cortisone injections or surgeries, most people can experience quick relief and eventual recovery with the right combination of non-invasive therapies.
Symptoms
Flat feet can exhibit a variety of symptoms, from mild to severe. The extent of the flat foto does not always correlate with the extent of symptoms. Patients may complain of arch pain and heel pain. Commonly there is pain on the outside of the foot, where the foot meets the ankle as the collapse foot abuts against the ankle. Muscle cramps within the foot, and onto the leg (shin splints) may occur. In general, patients have pain with activity, such as walking or running. The pain may be deep and focal to a generalized widespread achy feeling. Irritation from shoe gear can cause redness and swelling. Common reasons patients seek treatment are pain, interference with walking or activities, difficulty fitting shoes, swelling, and notice a change in appearance of the foot and/or unsightly appearance.
Diagnosis
The adult acquired flatfoot, secondary to posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, is diagnosed in a number of ways with no single test proven to be totally reliable. The most accurate diagnosis is made by a skilled clinician utilizing observation and hands on evaluation of the foot and ankle. Observation of the foot in a walking examination is most reliable. The affected foot appears more pronated and deformed compared to the unaffected foot. Muscle testing will show a strength deficit. An easy test to perform in the office is the single foot raise.
Non Surgical Treatment
The treatment is to put an arch support under the foot immediately to prevent the arch from collapsing and the plantar fascia from stretching. Also, put an arch support in your slippers and wear them as soon as you rise. Even a few steps barefoot without support can stretch the plantar fascia. Arch supports usually relieve pain within a few days. To head off arch pain, begin an exercise routine slowly, take off any excess weight and wear arch supports in your athletic shoes. Arch pain commonly smolders for months because people do not take the proper precautions. Continuing to do weight-bearing exercises will perpetuate the pain. While the foot is recovering, swim or do water workouts. Or work the upper body only. Some people are able to use a stationary bicycle by placing only the front part of the foot on the pedals.

Surgical Treatment
Fallen arches may occur with deformities of the foot bones. Tarsal coalition is a congenital condition in which the bones of the foot do not separate from one another during development in the womb. A child with tarsal coalition exhibits a rigid flat foot, which can be painful, notes the patient information website eOrthopod. Surgery may prove necessary to separate the bones. Other foot and ankle conditions that cause fallen arches may also require surgery if noninvasive treatments fail to alleviate pain and restore normal function.
Prevention
Because most cases of flatfeet are inherited, the condition is usually impossible to prevent. Even when children with flexible flatfeet are treated with arch supports and corrective shoes, there is little evidence that these devices prevent the condition from lasting into adulthood.
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Physical Therapy Exercises
Overview
Dysfunction of the tibialis posterior tendon is a common condition and a common cause of acquired flatfoot deformity in adults. Women older than 40 are most at risk. Patients present with pain and swelling of the medial hindfoot. Patients may also report a change in the shape of the foot or flattening of the foot. The foot develops a valgus heel (the heel rotates laterally when observed from behind), a flattened longitudinal arch, and an abducted forefoot. Conservative treatment includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, rest, and immobilisation for acute inflammation; and orthoses to control the more chronic symptoms. Surgical treatment in the early stages is hindfoot osteotomy combined with tendon transfer. Arthrodesis of the hindfoot, and occasionally the ankle, is required in the surgical treatment of the later stages of tibialis posterior dysfunction. 
Causes
There are numerous causes of acquired adult flatfoot, including fracture or dislocation, tendon laceration, tarsal coalition, arthritis, neuroarthropathy, neurologic weakness, and iatrogenic causes. The most common cause of acquired adult flatfoot is posterior tibial tendon dysfunction.
Symptoms
The symptom most often associated with AAF is PTTD, but it is important to see this only as a single step along a broader continuum. The most important function of the PT tendon is to work in synergy with the peroneus longus to stabilize the midtarsal joint (MTJ). When the PT muscle contracts and acts concentrically, it inverts the foot, thereby raising the medial arch. When stretched under tension, acting eccentrically, its function can be seen as a pronation retarder. The integrity of the PT tendon and muscle is crucial to the proper function of the foot, but it is far from the lone actor in maintaining the arch. There is a vital codependence on a host of other muscles and ligaments that when disrupted leads to an almost predictable loss in foot architecture and subsequent pathology.
Diagnosis
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction is diagnosed with careful clinical observation of the patient?s gait (walking), range of motion testing for the foot and ankle joints, and diagnostic imaging. People with flatfoot deformity walk with the heel angled outward, also called over-pronation. Although it is normal for the arch to impact the ground for shock absorption, people with PTTD have an arch that fully collapses to the ground and does not reform an arch during the entire gait period. After evaluating the ambulation pattern, the foot and ankle range of motion should be tested. Usually the affected foot will have decreased motion to the ankle joint and the hindfoot. Muscle strength may also be weaker as well. An easy test to perform for PTTD is the single heel raise where the patient is asked to raise up on the ball of his or her effected foot. A normal foot type can lift up on the toes without pain and the heel will invert slightly once the person has fully raised the heel up during the test. In early phases of PTTD the patient may be able to lift up the heel but the heel will not invert. An elongated or torn posterior tibial tendon, which is a mid to late finding of PTTD, will prohibit the patient from fully rising up on the heel and will cause intense pain to the arch. Finally diagnostic imaging, although used alone cannot diagnose PTTD, can provide additional information for an accurate diagnosis of flatfoot deformity. Xrays of the foot can show the practitioner important angular relationships of the hindfoot and forefoot which help diagnose flatfoot deformity. Most of the time, an MRI is not needed to diagnose PTTD but is a tool that should be considered in advanced cases of flatfoot deformity. If a partial tear of the posterior tibial tendon is of concern, then an MRI can show the anatomic location of the tear and the extensiveness of the injury.
Non surgical Treatment
This condition may be treated with conservative methods. These can include orthotic devices, special shoes, and bracing. Physical therapy, rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medication may be prescribed to help relieve symptoms. If the condition is very severe, surgical treatment may be needed. 
Surgical Treatment
In cases of PTTD that have progressed substantially or have failed to improve with non-surgical treatment, surgery may be required. For some advanced cases, surgery may be the only option. Your foot and ankle surgeon will determine the best approach for you.
How To Treat A Sore Achilles Tendon
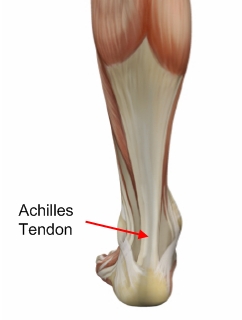 The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscles in the lower leg to the heel bone. It is the largest yet most exposed tendon in the body. Achilles tendonitis is where the Achilles tendon, and sometimes the protective sheath through which it moves, becomes inflamed, causing pain and swelling symptoms. Achilles tendonitis (also known as Achilles tendinopathy or tendonosis) is classified as an overuse injury. If left untreated it can become chronic (long-term), requiring more intensive treatment. Achilles tendonitis can also increase the risk of sustaining an Achilles tendon rupture (tear).
The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscles in the lower leg to the heel bone. It is the largest yet most exposed tendon in the body. Achilles tendonitis is where the Achilles tendon, and sometimes the protective sheath through which it moves, becomes inflamed, causing pain and swelling symptoms. Achilles tendonitis (also known as Achilles tendinopathy or tendonosis) is classified as an overuse injury. If left untreated it can become chronic (long-term), requiring more intensive treatment. Achilles tendonitis can also increase the risk of sustaining an Achilles tendon rupture (tear).
Causes
There are hundreds of tendons scattered throughout our body, but it tends to be a small handful of specific tendons that cause problems. These tendons usually have an area of poor blood supply that leads to tissue damage and poor healing response. This area of a tendon that is prone to injury is called a "watershed zone," an area when the blood supply to the tendon is weakest. In these watershed zones, they body has a hard time delivering oxygen and nutrients necessary for tendon healing, that's why we see common tendon problems in the same parts of the body. Tendonitis is most often an overuse injury. Often people begin a new activity or exercise that causes the tendon to become irritated. Tendon problems are most common in the 40-60 year old age range. Tendons are not as elastic and forgiving as in younger individuals, yet bodies are still exerting with the same force. Occasionally, there is an anatomical cause for tendonitis. If the tendon does not have a smooth path to glide along, it will be more likely to become irritated and inflamed. In these unusual situations, surgical treatment may be necessary to realign the tendon.
Symptoms
If you have Achilles tendinitis or Achilles enthesopathy, you are likely to experience the following symptoms. Pain. You may notice aching, burning, or tearing pains at the back of your heel or above the ankle. The pain can range from mild to very severe and disabling. It is most noticeable in the following circumstances. After resting. Many people report that pain increases when they first get out of bed in the morning or after sitting for a period of time. After exercise. Pain may increase if you exercise or stand for a period of time. A lump. In some cases, a tender lump can develop at the site of the injured tendon (tendinosis). Bone spurs. When the injury occurs at the point where the tendon attaches to the foot, a bone spur may develop on the heel.
Diagnosis
On examination, an inflamed or partially torn Achilles tendon is tender when squeezed between the fingers. Complete tears are differentiated by sudden, severe pain and inability to walk on the extremity. A palpable defect along the course of the tendon. A positive Thompson test (while the patient lies prone on the examination table, the examiner squeezes the calf muscle; this maneuver by the examiner does not cause the normally expected plantar flexion of the foot).
Nonsurgical Treatment
Self-care strategies include the following steps, often known by the acronym R.I.C.E, Rest. You may need to avoid exercise for several days or switch to an activity that doesn't strain the Achilles tendon, such as swimming. In severe cases, you may need to wear a walking boot and use crutches. Ice. To decrease pain or swelling, apply an ice pack to the tendon for about 15 minutes after exercising or when you experience pain. Compression. Wraps or compressive elastic bandages can help reduce swelling and reduce movement of the tendon. Elevation. Raise the affected foot above the level of your heart to reduce swelling. Sleep with your affected foot elevated at night.

Surgical Treatment
There are two types of Achilles repair surgery for tendonitis (inflammation of the Achilles Tendon), if nonsurgical treatments aren't effective. Gastrocnemius recession - The orthopaedic surgeon lengthens the calf muscles to reduce stress on your Achilles tendon. D?bridement and repair - During this procedure, the surgeon removes the damaged part of the Achilles tendon and repairs the remaining tendon with sutures or stitches. Debridement is done when the tendon has less than 50% damage.
Prevention
Wear shoes that fit correctly and support your feet: Replace your running or exercise shoes before the padding or shock absorption wears out. Shock absorption greatly decreases as the treads on the bottoms or sides of your shoes begin to wear down. You may need running shoes that give your foot more heel or arch support. You may need shoe inserts to keep your foot from rolling inward. Stretch before you exercise: Always warm up your muscles and stretch gently before you exercise. Do cool down exercises when you are finished. This will loosen your muscles and decrease stress on your Achilles tendon. Exercise the right way: If your tendinitis is caused by the way that you exercise, ask a trainer, coach, or your caregiver for help. They can teach you ways to train or exercise to help prevent Achilles tendinitis. Do not run or exercise on uneven or hard surfaces. Instead, run on softer surfaces such as treadmills, rubber tracks, grass, or evenly packed dirt tracks.